Simple Flying has previously discussed the small but mighty HondaJet, as it is particularly notable within the very-light business jet class. Although well-known for its efficiency, speed, and overall flight performance, what advancements have made this aircraft so capable?
1 Over-The-Wing Mounted Engines
You almost always find large components like jet engines under the wings or near the rear of the fuselage (there are a few exceptions, including but not limited to the VFW-Fokker 614, Boeing YC-14, and some Antonov planes), as smooth air flowing over the wings is required for lift. But for the HondaJet, its team poured research into an Over-The-Wing Engine Mount (OTWEM) configuration that still achieves substantial aerodynamic performance.
This has a couple of key benefits. For instance, business jets typically have rear-mounted engines, requiring large support structures; without these, the HondaJet has more cabin and luggage space. Additionally, over-the-wing engines naturally help reduce noise and vibration since they are positioned away from the fuselage.
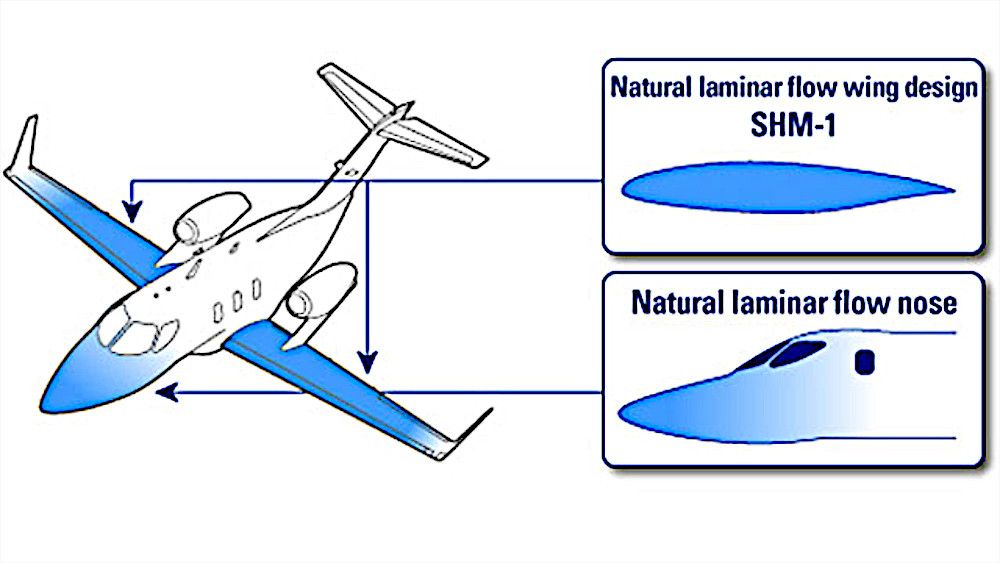
2 Natural Laminar Flow Wings and Nose
Laminar airflow refers to when airflow on a surface, such as an aircraft wing, is smooth, creating significantly less skin friction drag than turbulent flow. Honda has designed Natural Laminar Flow (NLF) wing and fuselage nose shapes to maintain this laminar flow during high-speed flight, delivering impressive speed and fuel efficiency.
With an optimized number and position of the different panels and rivets, surface irregularities are minimized, significantly suppressing aerodynamic drag.
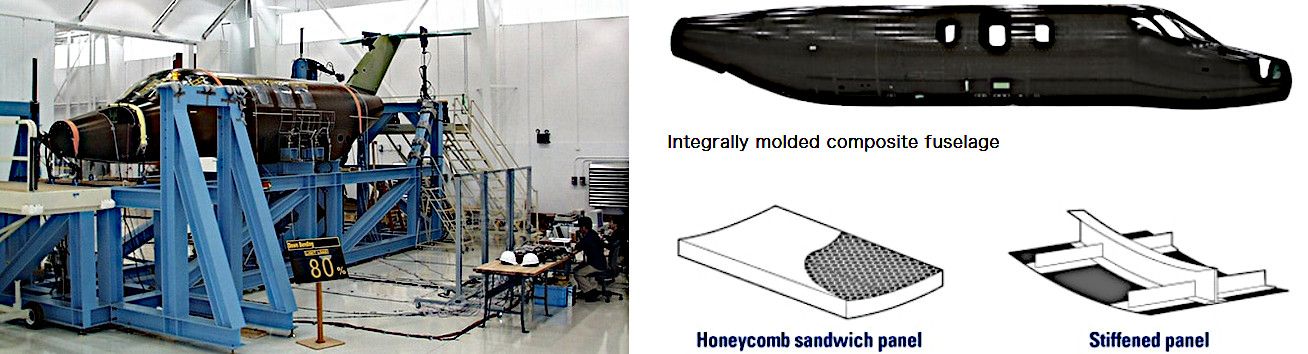
3 Integrally Molded Carbon Composite Fuselage
The HondaJet utilizes lightweight but strong carbon composite materials for its fuselage structure. Combining and integrally co-curing honeycomb sandwich panels with stiffened panels reduces aircraft weight and increases durability.
With its robust carbon composite fuselage, the HondaJet can fly safely at considerable altitudes for its class, which, as Honda suggests, has its own set of aerodynamic benefits compared to lower-altitude flight.
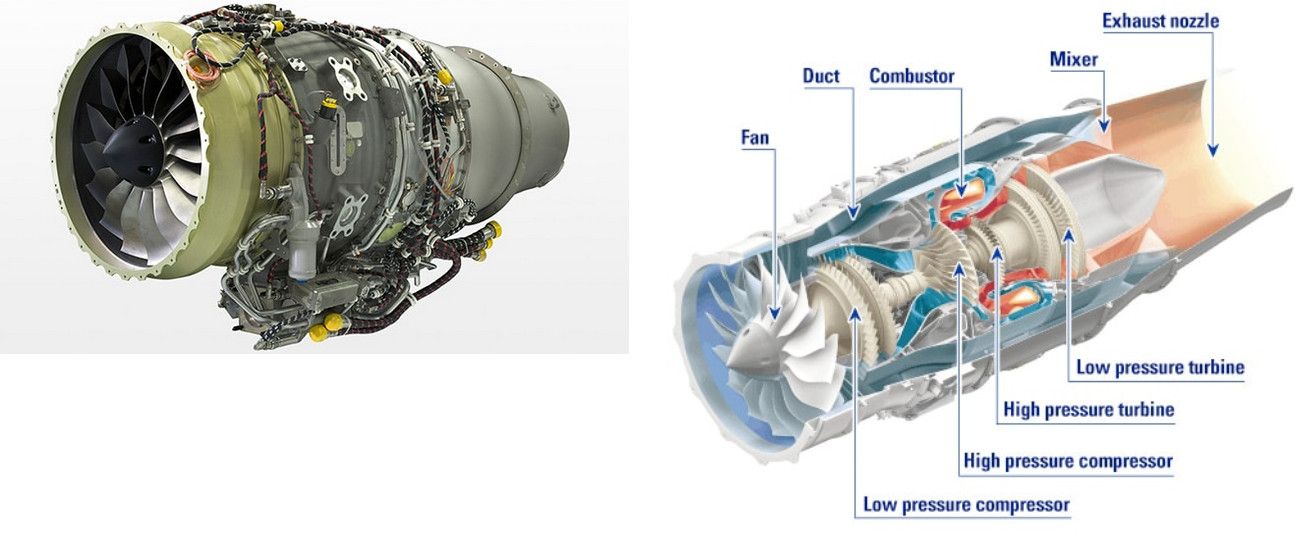
4 The HF120 Turbofan Engine
Not only is the engine placement a key innovation of the HondaJet, but the engines are also rather interesting. The GE Honda Aero Engine, HF120, is a lightweight, compact, high-thrust turbofan engine designed to meet current carbon emission and noise standards.
Despite a small diameter of approximately 53.8 cm (21.2 inches), the HF120 is potent and features a “Full Authority Digital Electronic Control” to achieve high efficiency and reliability.
5 Advanced cockpit and cabin space
Business jets must be powerful and deliver an enjoyable experience for its pilots and passengers, and the HondaJet does not disappoint. Its cockpit is based on research into ergonomics and human factors, featuring enhanced cockpit space, a wide-visibility windshield, and optimally positioned flight instruments and controls. Facilitating single-pilot operations, the HondaJet’s cockpit is intuitive, featuring the Garmin® G3000 next-gen avionics system with multiple 14-inch high-resolution displays and dual touch-screen controllers.
For passengers, business jets might be a workplace or a comfortable place for conversation and relaxation. Honda mentions its jet has a sophisticated interior design with completely adjustable executive seating, a fully private lavatory, and a class-leading seat pitch.
What do you think of these innovations? Have you ever flown in a HondaJet? Let us know in the comments below.
Source: Honda